浅谈Linux内核创建新进程的全过程
时间:2022-05-27 00:13:31|栏目:Linux|点击: 次
进程描述
- 进程描述符(task_struct)
用来描述进程的数据结构,可以理解为进程的属性。比如进程的状态、进程的标识(PID)等,都被封装在了进程描述符这个数据结构中,该数据结构被定义为task_struct
- 进程控制块(PCB)
是操作系统核心中一种数据结构,主要表示进程状态。
- 进程状态
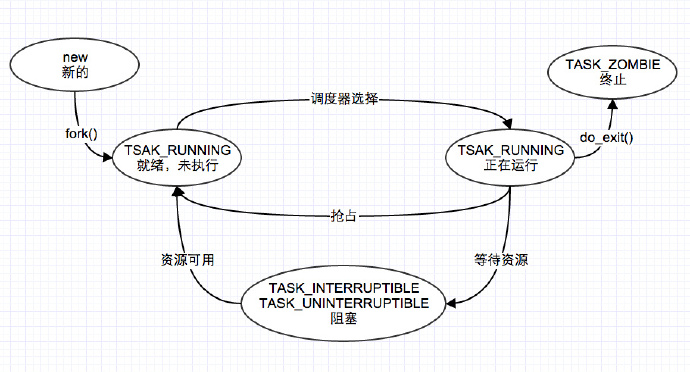
- fork()
fork()在父、子进程各返回一次。在父进程中返回子进程的 pid,在子进程中返回0。
fork一个子进程的代码
#include#include #include int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int pid; /* fork another process */ pid = fork(); if (pid < 0) { /* error occurred */ fprintf(stderr,"Fork Failed!"); exit(-1); } else if (pid == 0) { /* child process */ printf("This is Child Process!n"); } else { /* parent process */ printf("This is Parent Process!n"); /* parent will wait for the child to complete*/ wait(NULL); printf("Child Complete!n"); } }
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 06-17Linux进程信号的发送和保存方法
- 06-17Linux卸载自带jdk并安装新jdk版本的图文教程
- 06-17Linux系统中卸载与安装JDK的详细教程
- 06-17Linux系统配置NAT网络模式的详细步骤(附图文)
- 06-17Linux中的计划任务(crontab)使用方式
- 06-17Apache配置域名跳转的详细步骤
- 06-17Linux fsync系统调用方式
- 06-17Linux磁盘扩容lvm的使用详解
- 06-17Linux与Windows跨平台文件共享的实现方案
- 06-17Linux如何实现给/根目录扩容




